Here you can browse the reference documentation for Skyramp client applications.

This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Reference
- 1: Architecture
- 2: CLI Commands
- 2.1: skyramp
- 2.2: cluster
- 2.3: completion
- 2.4: dashboard
- 2.5: deployer
- 2.5.1: clean
- 2.5.2: coverage
- 2.5.3: down
- 2.5.4: generate
- 2.5.4.1: kubernetes
- 2.5.5: status
- 2.5.6: up
- 2.6: init
- 2.6.1: mock
- 2.6.1.1: grpc
- 2.6.1.2: jsonrpc-http
- 2.6.1.3: jsonrpc-ws
- 2.6.1.4: rest
- 2.6.2: project
- 2.6.3: target
- 2.6.4: test
- 2.6.4.1: grpc
- 2.6.4.2: jsonrpc-http
- 2.6.4.3: jsonrpc-ws
- 2.6.4.4: rest
- 2.7: logs
- 2.8: mocker
- 2.8.1: apply
- 2.8.2: delete
- 2.8.3: generate
- 2.8.3.1: grpc
- 2.8.3.2: jsonrpc-http
- 2.8.3.3: jsonrpc-ws
- 2.8.3.4: rest
- 2.8.3.5: rest-protobuf
- 2.8.4: status
- 2.8.4.1: response
- 2.9: resolver
- 2.10: tester
- 2.10.1: curl
- 2.10.2: generate
- 2.10.2.1: graphql
- 2.10.2.2: grpc
- 2.10.2.3: rest
- 2.10.2.4: rest-protobuf
- 2.10.3: start
- 2.10.4: status
- 2.10.5: stop
- 2.11: validate
- 2.12: version
- 2.13: viz
- 3: Dashboard
- 4: Libraries
- 5: Resolver
- 6: VSCode Extension
1 - Architecture
Kubernetes Architecture

There are three main components that form the core of Skyramp:
- Skyramp Library
- Skyramp Worker
- Skyramp Clients
Skyramp Library
Skyramp exposes all the key abstractions needed for distributed testing through the Skyramp Library on the client side. The Skyramp Library interacts with the Skyramp Worker deployed in-cluster to implement service mocking and testing, available as Mocker and Tester respectively.
In addition to Mocker and Tester, there is a separate client side abstraction exposed by the Library — Deployer. Deployer allows you to deploy a subset of your application given a Helm Chart.
For inner dev loop testing you can access the functionality of the library through our Clients. Alternatively, you can directly use the libraries in your CI pipelines to create custom testing solutions.
Skyramp Worker
The Skyramp Worker implements the core functionality of Mocker and Tester. It is deployed via Helm into your cluster. You can communicate with the Worker either directly via the Library or by using Skyramp Clients. The Worker provides several management features that are useful for testing and development including running and managing mocks, generating load for tests, managing and visualizing tests and more.
Skyramp Clients
Skyramp provides a Terminal client and a VSCode Extension for inner dev loop testing.
Terminal Client
The Terminal Client has a comprehensive list of CLI Commands you can use in ad-hoc testing. To install, visit the Install Client page.
VSCode Extension
The VSCode Extension is a visual way to interact with Skyramp right from your development environment. For more info, visit the VSCode Extension page.
Cluster Orchestration
Skyramp supports Kubernetes for orchestration as shown in the architecture diagram.

2.1 - skyramp
skyramp
skyramp [flags]
Options
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- cluster - Manage Kubernetes clusters
- completion - Generate the autocompletion script for the specified shell
- dashboard - Manage dashboard
- deployer - Manage target services
- init - Create description template
- logs - Retrieve debug, usage, and cluster create logs
- mocker - Manage mocks
- resolver - Manage DNS Resolver
- tester - Manage tests
- validate - Validate description
- version - Show version
- viz - (beta) Run terminal UI for Skyramp

2.2 - cluster
skyramp cluster
skyramp cluster [flags]
Options
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.2.1 - create
skyramp cluster create
Create a new local cluster or register an existing Kubernetes cluster.
skyramp cluster create [flags]
Options
-d, --dashboard install dashboard
--listen-any Kind API server listens to any address, default is localhost
-l, --local local cluster
-n, --name string name of the cluster to be created
Options inherited from parent commands
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- cluster - Manage Kubernetes clusters

2.2.2 - current
skyramp cluster current
skyramp cluster current [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- cluster - Manage Kubernetes clusters

2.2.3 - ingress
skyramp cluster ingress
skyramp cluster ingress [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.2.3.1 - down
skyramp cluster ingress down
skyramp cluster ingress down [flags]
Options
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
--kubernetes-service string Kubernetes service list separated by comma
-n, --namespace string valid Kubernetes namespace
Options inherited from parent commands
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- ingress - Manage ingress

2.2.3.2 - up
skyramp cluster ingress up
skyramp cluster ingress up [flags]
Options
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
--kubernetes-service string Kubernetes service list separated by comma
-n, --namespace string valid Kubernetes namespace
--protocol string protocol to use for the ingress generation (one of [grpc rest thrift])
Options inherited from parent commands
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- ingress - Manage ingress

2.2.4 - list
skyramp cluster list
skyramp cluster list [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- cluster - Manage Kubernetes clusters

2.2.5 - register
skyramp cluster register
Register kubeconfig of a pre-provisioned cluster. Alternative to ‘skyramp config apply’.
skyramp cluster register <kubeconfig-file-path> [flags]
Options
--context string k8s context
-d, --dashboard install dashboard
--install-ingress deploy skyramp ingress controller
-n, --name string name of the cluster to be created
Options inherited from parent commands
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- cluster - Manage Kubernetes clusters

2.2.6 - remove
skyramp cluster remove
skyramp cluster remove [flags]
Options
-l, --local local cluster
-n, --name string name of the cluster to be removed
Options inherited from parent commands
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- cluster - Manage Kubernetes clusters

2.2.7 - switch
skyramp cluster switch
skyramp cluster switch <cluster name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--airgap enable airgap mode (only supported for local clusters)
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- cluster - Manage Kubernetes clusters

2.3 - completion
skyramp completion
skyramp completion <shell> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.3.1 - off
skyramp completion off
skyramp completion off <shell> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- completion - Generate the autocompletion script for the specified shell

2.3.2 - on
skyramp completion on
skyramp completion on <shell> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- completion - Generate the autocompletion script for the specified shell

2.4 - dashboard
skyramp dashboard
skyramp dashboard [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.4.1 - down
skyramp dashboard down
skyramp dashboard down [flags]
Options
-g, --grafana force dashboard installation/update
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- dashboard - Manage dashboard

2.4.2 - up
skyramp dashboard up
Bring up dashboard (Skyramp by default)
skyramp dashboard up [flags]
Options
-d, --docker open the Skyramp dashboard deployed on Docker
-f, --force force dashboard installation/update
-g, --grafana bring up Grafana dashboard
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- dashboard - Manage dashboard

2.5 - deployer
skyramp deployer
skyramp deployer [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- skyramp - Command line tool to interact with Skyramp
- clean - Remove all Kubernetes resources deployed by Skyramp
- coverage - Configures or retrieves coverage data
- down - Tear down target services
- generate - Generates configurations from an existing deployment
- status - Show details for deployed targets
- up - Bring up target services

2.5.1 - clean
skyramp deployer clean
Remove all Kubernetes resources deployed by Skyramp from a cluster. Note that this will not clean up the cluster(s) and infrastructure.
skyramp deployer clean [flags]
Options
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- deployer - Manage target services

2.5.2 - coverage
skyramp deployer coverage
skyramp deployer coverage [flags]
Options
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.5.2.1 - collect
skyramp deployer coverage collect
skyramp deployer coverage collect [flags]
Options
--api-schema strings schema file(s) to use for the coverage data
--code-coverage-out string output directory for the code coverage data (default "/tmp/cover")
--protocol string protocol to use for the schema files (one of [rest]) (default "rest")
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- coverage - Configures or retrieves coverage data

2.5.2.2 - restart
skyramp deployer coverage restart
skyramp deployer coverage restart <target-name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- coverage - Configures or retrieves coverage data

2.5.3 - down
skyramp deployer down
skyramp deployer down <target name> [flags]
Options
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
-f, --force force delete the target
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- deployer - Manage target services

2.5.4 - generate
skyramp deployer generate
skyramp deployer generate [flags]
Options
--api-coverage generate and pull API coverage data
--code-coverage generate and pull code coverage data
--protocol string protocol to use for the deployer configuration (one of [rest]) (default "rest")
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- deployer - Manage target services
- kubernetes - Generates configurations from an existing deployment in Kubernetes

2.5.4.1 - kubernetes
skyramp deployer generate kubernetes
skyramp deployer generate kubernetes [flags]
Options
--kubeconfig string path of the kubeconfig where
--namespace string namespace where the application is deployed
Options inherited from parent commands
--api-coverage generate and pull API coverage data
--code-coverage generate and pull code coverage data
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--protocol string protocol to use for the deployer configuration (one of [rest]) (default "rest")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generates configurations from an existing deployment

2.5.5 - status
skyramp deployer status
skyramp deployer status [flags]
Options
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- deployer - Manage target services

2.5.6 - up
skyramp deployer up
skyramp deployer up <target name> [flags]
Options
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
--local-images load local container images
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace
--skip-deploy-worker
--worker-image string worker image URL
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- deployer - Manage target services

2.6 - init
skyramp init
skyramp init [flags]
Options
-f, --force force create description
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.6.1 - mock
skyramp init mock
skyramp init mock [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- init - Create description template
- grpc - Create mock description for gRPC protocol
- jsonrpc-http - Create mock description for JSON-RPC over HTTP protocol
- jsonrpc-ws - Create mock description for JSON-RPC over WebSocket protocol
- rest - Create mock description for REST protocol

2.6.1.1 - grpc
skyramp init mock grpc
skyramp init mock grpc <mock name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- mock - Create mock description

2.6.1.2 - jsonrpc-http
skyramp init mock jsonrpc-http
skyramp init mock jsonrpc-http <mock name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- mock - Create mock description

2.6.1.3 - jsonrpc-ws
skyramp init mock jsonrpc-ws
skyramp init mock jsonrpc-ws <mock name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- mock - Create mock description

2.6.1.4 - rest
skyramp init mock rest
skyramp init mock rest <mock name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- mock - Create mock description

2.6.2 - project
skyramp init project
skyramp init project <project name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- init - Create description template

2.6.3 - target
skyramp init target
skyramp init target <target name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- init - Create description template

2.6.4 - test
skyramp init test
skyramp init test [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- init - Create description template
- grpc - Create test description for gRPC protocol
- jsonrpc-http - Create test description for JSON-RPC over HTTP protocol
- jsonrpc-ws - Create test description for JSON-RPC over WebSocket protocol
- rest - Create test description for REST protocol

2.6.4.1 - grpc
skyramp init test grpc
skyramp init test grpc <test name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- test - Create test description

2.6.4.2 - jsonrpc-http
skyramp init test jsonrpc-http
skyramp init test jsonrpc-http <test name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- test - Create test description

2.6.4.3 - jsonrpc-ws
skyramp init test jsonrpc-ws
skyramp init test jsonrpc-ws <test name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- test - Create test description

2.6.4.4 - rest
skyramp init test rest
skyramp init test rest <test name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
-f, --force force create description
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- test - Create test description

2.7 - logs
skyramp logs
skyramp logs [flags]
Examples
skyramp logs container-name -t target-name # Get debug logs
skyramp logs --cluster-create # Get cluster create logs
Options
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
--cluster-create retrieve logs from cluster creation
-f, --follow stream logs
-t, --target string target which will contain the container
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- skyramp - Command line tool to interact with Skyramp

2.8 - mocker
skyramp mocker
skyramp mocker [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.8.1 - apply
skyramp mocker apply
skyramp mocker apply <mock file> [flags]
Examples
skyramp mocker apply -n namespace # Apply mocks to the worker container running on Kubernetes
skyramp mocker apply -a localhost:35142 # Apply mocks to the worker container running on Docker
Options
-a, --address string ip:port of Skyramp worker
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
--endpoint string endpoint to use for mocking
--method string method to use for mocking (endpoint argument must be specified)
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
--value string response value to use for mocking (endpoint and method arguments must be specified)
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- mocker - Manage mocks

2.8.2 - delete
skyramp mocker delete
skyramp mocker delete [flags]
Examples
skyramp mocker delete -a localhost:35142 # Delete mocks from the worker container running on Docker
Options
-a, --address string ip:port of Skyramp worker
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- mocker - Manage mocks

2.8.3 - generate
skyramp mocker generate
skyramp mocker generate [flags]
Options
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate mock values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-context string (experimental) Optional, extra context to give OpenAI to augment the mock values
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--port int port number for the service
--sample-response string path to API sample response file
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- mocker - Manage mocks
- grpc - Generate mock configurations for gRPC protocol
- jsonrpc-http - Generate mock configurations for JSON-RPC over HTTP protocol
- jsonrpc-ws - Generate mock configurations for JSON-RPC over Websocket protocol
- rest - Generate mock configurations for REST protocol
- rest-protobuf - Generate mock configurations for REST protocol using protobuf

2.8.3.1 - grpc
skyramp mocker generate grpc
skyramp mocker generate grpc [flags]
Examples
skyramp mocker generate grpc --api-schema path/to/schema.proto --alias my-service --port 8080 --service ProductService
Options
--service string proto service to utilize
Options inherited from parent commands
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate mock values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-context string (experimental) Optional, extra context to give OpenAI to augment the mock values
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--port int port number for the service
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--sample-response string path to API sample response file
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generate mock configurations

2.8.3.2 - jsonrpc-http
skyramp mocker generate jsonrpc-http
skyramp mocker generate jsonrpc-http [flags]
Examples
skyramp mocker generate jsonrpc-http --sample-response path/to/sample-response.json --alias my-service --port 8080 --endpoint-path /api/v1 --method calculateSum
Options
--endpoint-path string the REST path that upgrades http to a websocket
--method string json-rpc method to utilize
Options inherited from parent commands
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate mock values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-context string (experimental) Optional, extra context to give OpenAI to augment the mock values
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--port int port number for the service
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--sample-response string path to API sample response file
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generate mock configurations

2.8.3.3 - jsonrpc-ws
skyramp mocker generate jsonrpc-ws
skyramp mocker generate jsonrpc-ws [flags]
Examples
skyramp mocker generate jsonrpc-ws --sample-response path/to/sample-response.json --alias my-service --port 8080 --endpoint-path /api/v1 --method calculateSum
Options
--endpoint-path string the REST path that upgrades http to a websocket
--method string json-rpc method to utilize
Options inherited from parent commands
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate mock values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-context string (experimental) Optional, extra context to give OpenAI to augment the mock values
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--port int port number for the service
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--sample-response string path to API sample response file
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generate mock configurations

2.8.3.4 - rest
skyramp mocker generate rest
skyramp mocker generate rest [flags]
Examples
skyramp mocker generate rest --api-schema https://example.com/api/v1/openapi.yaml --alias my-service --port 8080 --tag users --paths /api/v1/users
skyramp mocker generate rest --sample-response path/to/sample-response.json --alias my-service --port 8080 --endpoint-path /api/v1
Options
--endpoint-path string the REST path that upgrades http to a websocket
--path strings REST path to filter on. Can be used multiple times to filter on multiple paths.
--paths string comma-separated list of REST paths to filter on (to be deprecated: use --path instead)
--tag string OpenAPI tag to filter on
Options inherited from parent commands
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate mock values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-context string (experimental) Optional, extra context to give OpenAI to augment the mock values
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--port int port number for the service
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--sample-response string path to API sample response file
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generate mock configurations

2.8.3.5 - rest-protobuf
skyramp mocker generate rest-protobuf
skyramp mocker generate rest-protobuf [flags]
Options
--api-schemas strings paths to API schema file
--proto-path string proto_path to use for parsing multiple protobuf files
--protobuf-any stringToString map of the location of a protobuf any type to the value to the type to replace the type (default [])
--service string proto service to utilize
Options inherited from parent commands
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate mock values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-context string (experimental) Optional, extra context to give OpenAI to augment the mock values
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--port int port number for the service
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--sample-response string path to API sample response file
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generate mock configurations

2.8.4 - status
skyramp mocker status
skyramp mocker status [flags]
Options
-a, --address string ip:port of Skyramp worker
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
-e, --endpoint string endpoint name to filter on
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.8.4.1 - response
skyramp mocker status response
skyramp mocker status response [flags]
Options
-a, --address string ip:port of Skyramp worker
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
-e, --endpoint string endpoint name to filter on
-i, --id string ID from mocker status table to query response value
-m, --method string method name to query response value
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- status - Show applied mocks on the running worker container

2.9 - resolver
skyramp resolver
skyramp resolver [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.9.1 - add
skyramp resolver add
skyramp resolver add [flags]
Options
--domain string domain
--ip string ip
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- resolver - Manage DNS Resolver

2.9.2 - remove
skyramp resolver remove
skyramp resolver remove [flags]
Options
--domain string domain
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- resolver - Manage DNS Resolver

2.9.3 - start
skyramp resolver start
skyramp resolver start [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- resolver - Manage DNS Resolver

2.9.4 - status
skyramp resolver status
skyramp resolver status [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- resolver - Manage DNS Resolver

2.9.5 - stop
skyramp resolver stop
skyramp resolver stop [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- resolver - Manage DNS Resolver

2.10 - tester
skyramp tester
skyramp tester [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- skyramp - Command line tool to interact with Skyramp
- curl - Execute a single http request in the running worker container
- generate - Generate test configurations
- start - Starts a test description in the running worker container
- status - Shows all tests in progress in the running worker container
- stop - Stops a test description in the running worker container

2.10.1 - curl
skyramp tester curl
skyramp tester curl <request file> [flags]
Options
-a, --address string ip:port of Skyramp worker
--data string request payload for curl execution
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- tester - Manage tests

2.10.2 - generate
skyramp tester generate
skyramp tester generate [flags]
Examples
skyramp tester generate --cluster-id cluster-id --namespace namespace --start-time "-5m" --telemetry-provider pixie
skyramp tester generate --trace-file trace-file.json
Options
--address string destination address of tests
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
--cluster-id string cluster id from telemetry provider
-f, --force force create test configurations and overwrite existing files
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate test values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--output-prefix string prefix for generated files
--port int port number for the service
--start-time string start time to retrieve traces from
--telemetry-provider string telemetry provider, currently only pixie is supported
--trace-file string trace file path
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- tester - Manage tests
- graphql - Generate test configurations for Graphql protocol
- grpc - Generate test configurations for gRPC protocol
- rest - Generate test configurations for REST protocol
- rest-protobuf - Generate test configurations for REST protocol with a Protobuf schema definition

2.10.2.1 - graphql
skyramp tester generate graphql
skyramp tester generate graphql [flags]
Options
--graphql-url-path string graphql http url path
--graphql-ws-path string graphql ws url path
Options inherited from parent commands
--address string destination address of tests
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
--cluster-id string cluster id from telemetry provider
-f, --force force create test configurations and overwrite existing files
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate test values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--output-prefix string prefix for generated files
--port int port number for the service
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--start-time string start time to retrieve traces from
--telemetry-provider string telemetry provider, currently only pixie is supported
--trace-file string trace file path
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generate test configurations

2.10.2.2 - grpc
skyramp tester generate grpc
skyramp tester generate grpc [flags]
Examples
skyramp tester generate grpc --api-schema path/to/your.proto --alias my-service --port 8080 --service ProductService
Options
--service string proto service to utilize
Options inherited from parent commands
--address string destination address of tests
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
--cluster-id string cluster id from telemetry provider
-f, --force force create test configurations and overwrite existing files
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate test values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--output-prefix string prefix for generated files
--port int port number for the service
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--start-time string start time to retrieve traces from
--telemetry-provider string telemetry provider, currently only pixie is supported
--trace-file string trace file path
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generate test configurations

2.10.2.3 - rest
skyramp tester generate rest
skyramp tester generate rest [flags]
Examples
skyramp tester generate rest --api-schema https://example.com/api/v1/openapi.yaml --alias my-service --port 8080 --tag users --paths /users
Options
--endpoint-path string the REST path that upgrades http to a websocket
--negative-scenarios generate negative test scenarios for REST endpoints (default true)
--no-functional-scenarios disable generating functional scenarios for REST endpoints
--no-negative-scenarios disable generating negative test scenarios for REST endpoints
--path strings REST path to filter on. Can be used multiple times to filter on multiple paths.
--paths string comma-separated list of REST paths to filter on (to be deprecated: use --path instead)
--robot generate robot tests
--sample-form-param strings sample form parameter for REST endpoints in key=value format
--sample-query-param strings sample query parameter for REST endpoints in key=value format
--sample-request string path to API sample request file
--tag string OpenAPI tag to filter on
Options inherited from parent commands
--address string destination address of tests
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
--cluster-id string cluster id from telemetry provider
-f, --force force create test configurations and overwrite existing files
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate test values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--output-prefix string prefix for generated files
--port int port number for the service
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--start-time string start time to retrieve traces from
--telemetry-provider string telemetry provider, currently only pixie is supported
--trace-file string trace file path
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generate test configurations

2.10.2.4 - rest-protobuf
skyramp tester generate rest-protobuf
skyramp tester generate rest-protobuf [flags]
Options
--api-schemas strings paths to API schema file
--proto-path string proto_path to use for parsing multiple protobuf files
--protobuf-any stringToString map of the location of a protobuf any type to the value to the type to replace the type (default [])
--service string proto service to utilize
Options inherited from parent commands
--address string destination address of tests
--alias string Kubernetes service / Docker alias name
--api-schema string path to API schema file, or URL (URL support for OpenAPI 3.x only)
--cluster-id string cluster id from telemetry provider
-f, --force force create test configurations and overwrite existing files
-g, --glyphs string Specify the glyph combination to use: "1,2,3" - 1.Chinese 2.Cedilla 3.Emoji 4.Korean 5.German 6.French 7.Spanish 8.Russian 9.Control Char
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
--language string specify output language for Skyramp library code generation. Accepted values: "python" (default "YAML")
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
--openai (experimental) use OpenAI to generate test values (the 'OPENAI_API_KEY' environment variable must be set with an OpenAI API token)
--openai-model string (experimental) Optional, GPT model to use for OpenAI (one of [gpt-3.5-turbo gpt-4]). Note that some models may not accessible based on the API token (default "gpt-3.5-turbo")
--output-prefix string prefix for generated files
--port int port number for the service
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
--start-time string start time to retrieve traces from
--telemetry-provider string telemetry provider, currently only pixie is supported
--trace-file string trace file path
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- generate - Generate test configurations

2.10.3 - start
skyramp tester start
skyramp tester start <test description> [flags]
Examples
skyramp tester start mytest -n my-namespace # Start a test in the worker container running on Kubernetes
skyramp tester start mytest -a localhost:35142 # Start a test in the worker container running on Docker
Options
-a, --address string ip:port of Skyramp worker
--at-once int set number of threads for load test, default is 1
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
--duration string set duration for load test (e.g., 1s, 1m, 1h)
-f, --fail return non zero for failed tests
--html-report generate an HTML test report in the "results" directory
--local-images load local container images
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
--override strings override values for skyramp objects
--override-file string override value file path for skyramp objects
--set strings set values for globalVars
--stdout print results to stdout
--truncate truncate responses in terminal logging
--worker-image string worker image URL
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- tester - Manage tests

2.10.4 - status
skyramp tester status
skyramp tester status <test description> [flags]
Options
-a, --address string ip:port of Skyramp worker
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
--id string tester id
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- tester - Manage tests

2.10.5 - stop
skyramp tester stop
skyramp tester stop <test description> [flags]
Options
-a, --address string ip:port of Skyramp worker
-c, --cluster string cluster context for Skyramp
--id string tester id
-n, --namespace string Kubernetes namespace where Skyramp worker resides
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- tester - Manage tests

2.11 - validate
skyramp validate
skyramp validate [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
2.11.1 - mock
skyramp validate mock
skyramp validate mock <mock name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- validate - Validate description

2.11.2 - target
skyramp validate target
skyramp validate target <target name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- validate - Validate description

2.11.3 - test
skyramp validate test
skyramp validate test <test name> [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- validate - Validate description

2.12 - version
skyramp version
skyramp version [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- skyramp - Command line tool to interact with Skyramp

2.13 - viz
skyramp viz
skyramp viz [flags]
Options inherited from parent commands
--kube-insecure enable insecure mode for interactions with Kubernetes clusters
-p, --project-path string path to Skyramp project folder (default ".")
-v, --verbose count verbose (-v or -vv)
SEE ALSO
- skyramp - Command line tool to interact with Skyramp

3 - Dashboard
Welcome to the Skyramp Dashboard documentation. This guide will walk you through deploying and utilizing the Skyramp Dashboard on your Kubernetes cluster, allowing you to efficiently manage test results, mocks, and maintain records of your test runs.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure your Kubernetes cluster is registered with Skyramp. If it isn’t, you can configure it using either the skyramp cluster create or skyramp cluster register commands. Verify your cluster configuration by running:
skyramp cluster current
Bringing Up the Dashboard
To bring up the Skyramp Dashboard for Kubernetes deployments, execute the following command:
skyramp dashboard up
This command automates the deployment process, creating essential Kubernetes assets (client, server, and MongoDB Kubernetes Operator) within the skyramp namespace of your cluster. It also initiates port forwarding for local access. Once the dashboard is live, the terminal client will provide the forwarding address:
...
The dashboard is accessible here: http://localhost:53430/testresults
Port forwarding is started for the dashboard, hit Ctrl+c (or Cmd+c) to stop
No manual opening of this address in your browser is required; it should be done automatically.
Note
For a Grafana dashboard instead, use the--grafana (shorthand: -g) option in the skyramp dashboard up command.
All the flags available for skyramp dashboard can be found on the CLI Commands page.
Viewing the Dashboard
Running skyramp dashboard up will open the dashboard in a new browser tab. If you’re starting fresh without previous test runs, you’ll see an empty test result page:

Analyzing Test Results
Once your dashboard is running, you can use Tester to execute tests in-cluster and view the results automatically on the dashboard. For example, if you start the Checkout system testcase and a Checkout system load test testcase, they will then appear in the Test Results section of the dashboard:

From the Test Results page of the dashboard, you can click through to the Checkout system testcase to see the functional test results, including output, errors, duration, and status:

Navigate to the Checkout system load test testcase to view the load test results:

You can scroll down and view various load-related outputs and graphs related to latency, error rate, requests per second (RPS), and pod-specific utilization. Dashboard test results are valuable for retaining test run history and sharing among team members on a shared cluster.
Tracking Active Mocks
Once your dashboard is running, you can use Mocker to apply mocks in-cluster and track active mocks. For example, if you mock the payment-service with skyramp mocker apply, you can view active mocks and responses in the Mocked Services section:

This is particularly useful when managing multiple mocks across teams on a shared cluster and keeping track of the payloads for each endpoint.
Bringing Down the Dashboard
To stop the dashboard and clean up Kubernetes manifests, run the following command:
skyramp dashboard down
You are now ready to efficiently manage your testing environment with the Skyramp Dashboard!

4 - Libraries
Python
How to install the Skyramp Python library:
pip install skyramp
Visit the PyPI module page for more info.
JavaScript
How to install the Skyramp JavaScript library:
npm install skyramp
Visit the NPM module page for more info.

5 - Resolver
Skyramp runs a Dnsmasq container, called Resolver, on the local machine to resolve addresses under the skyramp.test domain. Resolver can also be used to configure access to other kubernetes clusters not managed by Skyramp.
Resolver uses port mapping 5553:53 on MAC and 53:53 on WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux), and is automatically started when new domain configurations are added.
Before you begin
Resolver commands can be triggered via the Skyramp binary. Follow instructions here to install Skyramp.
Resolver works out of the box on Linux, macOS, and WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux). To use it on Windows, follow the additional configuration steps.
Start Resolver
Skyramp automatically starts Resolver in two cases:
- when a cluster is brought up by Skyramp.
- when a new configuration is added to Resolver via the
config addcommand.
To force start Resolver, you can run the following command:
skyramp resolver start
NOTE
If you are using WSL you must re-run this command when WSL is restarted or if the host network changes.
Failure to configure the DNS correctly will result in requests not reaching the test cluster.
Add domain
As noted earlier, the skyramp.test domain is automatically added to Resolver for clusters brought up by Skyramp. To add a new domain, run the following command:
skyramp resolver config add --domain <domain> --ip <ip>
Based on the Operating System you are on, Skyramp makes the appropriate configurations as follows:
MAC : A new domain configuration is created in the /etc/resolver directory for each configured domain.
Linux (Ubuntu): Skyramp updates the configuration file at /etc/systemd/resolved.conf with the IP of the resolver container and restarts the systemd-resolved service.
Windows: Skyramp updates the configuration file at /etc/resolv.conf with the Resolver container as the first nameserver.
View configuration
You can view all DNS resolutions configured by Resolver by running:
skyramp resolver config show
Verify configuration
Test the configuration by performing a ping to any configured domain.
ping -c 1 <domain>
Example result:
PING <domain> (127.0.0.1): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from 127.0.0.1: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=0.033 ms
--- <domain> ping statistics ---
1 packets transmitted, 1 packets received, 0.0% packet loss
round-trip min/avg/max/stddev = 0.033/0.033/0.033/0.000 ms
Remove domain
List configured domains for the skyramp resolver by running:
skyramp resolver config remove --domain <domain>
Stop Resolver
You can stop Resolver at any time by running the stop command.
skyramp resolver stop
Windows Configuration
While Resolver works out of the box on WSL, additional configuration is needed to use it on Windows.
- Download Resolver on WSL by following the documentation for installing Skyramp.
- Download and install Docker Desktop.
- Ensure that Resolver is not running in WSL:
skyramp resolver stop. - On Windows, open
Settingsand selectNetwork & internetto view current DNS server configuration. - Edit
DNS Server Assignment, and selectManualDNS settings. - Set
Preferred DNSvalue to127.0.0.1andAlternate DNSto the primary DNS server as listed in step 2.
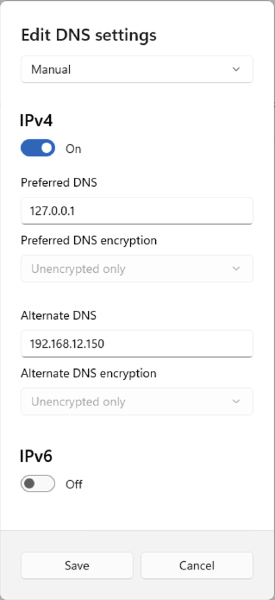
Windows Settings
All Resolver specific commands can be run inside WSL now.
Note
In case of issues with DNS resolution on the Windows machine, revert theDNS Server Assignment settings to Automatic.

6 - VSCode Extension
Easily isolate your services from surrounding dependencies and write and run integration and performance tests as you develop and debug, directly in VSCode. Visit the VSCode extension marketplace to download and install the extension.
Getting Started
1. Set Up a Kubernetes Cluster
First, run the Set Up Cluster command to configure a Kubernetes cluster to use with Mocker and Tester.

Note: Please be aware that provisioning a local cluster is supported only on MacOS or Linux. On Windows, you can only connect to an existing cluster.
2. Deploy New Worker Container
Next, install the Worker container in your cluster by running the Deploy New Worker Container command.

Mocker
How Mocker works
Mocker is an in-cluster solution for creating API mock servers. Refer to the Mocker page to learn more about how Mocker works. You can follow the following steps to use Mocker in the VS code extension:
1. Generate Mock
When you’re ready to mock a service, run the Generate Mock command to generate a mock configuration in the form of a .yaml file in the mocks folder of your working directory. You will be prompted to select an API schema file to mock against, and input some necessary configuration details including the Kubernetes service name, port number, and proto service name (if applicable).

Tip: We recommend running the generate command in your source code repo so mocks are versioned and shareable across your team.
2. Edit Mock
Mocker generates default values for responses based on the API signature. You can edit the default values by editing the generated mock in the mocks folder.

Note: Read more about writing mock configurations here
3. Apply Mock
Now, you can push the mock configuration to Mocker by running the Apply Mocks command:
 That’s it! All calls to the mocked service/s are now routed to Mocker and it responds with the default values in the configuration.
That’s it! All calls to the mocked service/s are now routed to Mocker and it responds with the default values in the configuration.
Note: Mocker does not automatically update the mocks when the responses are updated in the mock configuration file. You can run the
Apply Mockscommand again when your mock values change. Note: When mocking a gRPC service the container needs to be redeployed if the proto definition of the mock changes.
Tester
How Tester works
Tester is a solution that simplifies the process of both writing and running tests for complicated distributed apps. Refer to the Tester page to learn more about how Tester works. You can follow the following steps to use Tester in the VS code extension:
1. Generate Test
When you’re ready to test a service, run the Generate Test command to generate a test configuration in the form of a .yaml file in the tests folder of your working directory. You will be prompted to select an API schema file to test against, and input some necessary configuration details including the test name, Kubernetes service name, port number, and proto service name (if applicable).

2. Edit Test
Tester generates default values for requests based on the API signature. You can edit the default values and add request steps by editing the generated test in the tests folder.

Note: Read more about Tester and writing test configurations here
3. Start Test
Now, you can start the test configurations by running the Start Test command:
 That’s it! Tester will execute the test and output on the test results in the
That’s it! Tester will execute the test and output on the test results in the results output directory.
Requirements
Helm
The Worker container is installed in your cluster via Helm. In case you don’t have Helm installed, refer to Helm’s documentation to get started.

